본 post는 국가생명연구자원정보센터(KOBIC) 주관 서울대학교 의과대학 최무림 교수님의 WES 기초편 강의를 정리한 내용입니다.
Intro
Compound geterozygous, rare homozygous, hemizygous variants 의미를 이해합니다. 각 recessive variants에 맞는 filtering criteria를 이해합니다.
Trio-based Mendelian Disorder Research
 Trio-based Mendelian Disorder
Trio-based Mendelian Disorder
www.edwith.org/wes-beginner
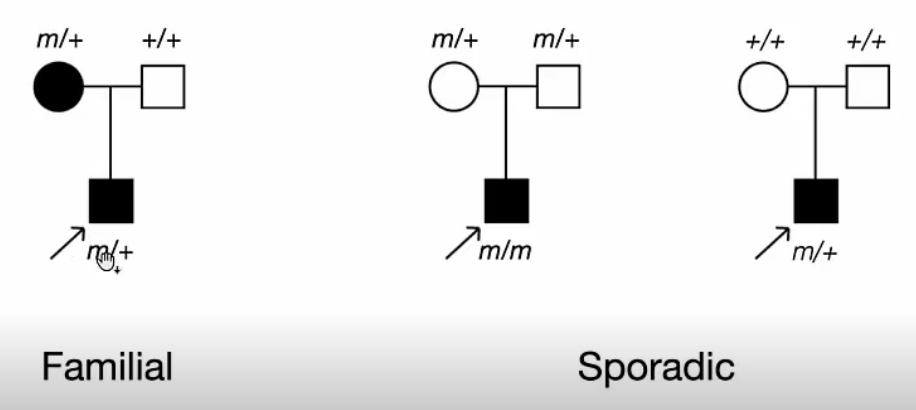
1번 pedigree는 부모 한 쪽에 dominant variant를 가지고 있어서 자녀에게도 disease가 유전된 경우를 보여주고 있습니다.
2번 pedigree는 부모 모두 하나의 allele에 variant를 가지고 있는 보인자 상태이고 자녀에게 variant를 가진 allele들이 유전되어 disease가 발현된 경우를 보여주고 있습니다.
3번 pedigree는 부모 모두 variant가 없고 정상이지만 자녀에게서 dominant variant가 발생하여 disease가 발현된 경우를 보여주고 있습니다.
1번, 3번 pedigree는 dominant variants 경우를, 2번은 recessive variants 경우를 보여주고 있습니다.
Dominant vs Recessive
 Dominant vs Recessive
Dominant vs Recessive
www.edwith.org/wes-beginner
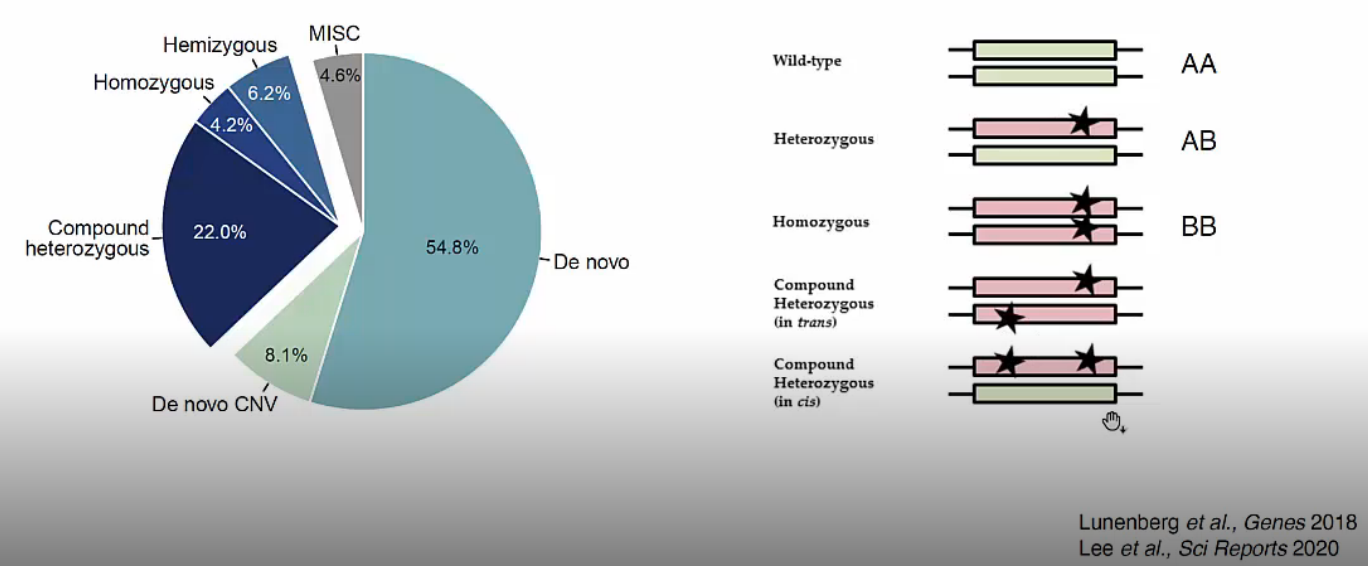
Dominant variants인 De novo variants와 De novo CNV(structural variants)가 약 2/3 가량, recessive variants인 나머지가 약 1/3 가량을 차지합니다.
Recessive variants는 오른쪽 그림과 같이 여러 가지 종류로 분류합니다. Compound Heterozygous는 두 개 variants가 멀리 떨어져 있는 경우 short read length의 illumina sequencer로는 in trans와 in cis를 구분하기 어렵습니다. 구분이 필요한 경우 long read를 사용하는 PacBio와 같은 sequencer로 해당 region을 sequencing 해야합니다.
- Heterozygous: 두 개 allele 중 하나의 allele에 variants가 존재하는 경우입니다.
- Homozygous: 두 개 allele 모두 같은 위치에서 variants가 존재하는 경우입니다.
- Compound Heterozygous (in trans): 하나의 gene에 두 개의 서로 다른 position에서의 variants가 각각 다른 allele에 존재하는 경우입니다.
- Compound Heterozygous (in cis): 하나의 gene에 두 개의 서로 다른 position에서의 variants가 동일한 allele에 존재하는 경우입니다.
 Dominant vs Recessive
Dominant vs Recessive
www.edwith.org/wes-beginner
Importance of Understanding Recessive Variants
 Importance of Understanding Recessive Variants
Importance of Understanding Recessive Variants
www.edwith.org/wes-beginner
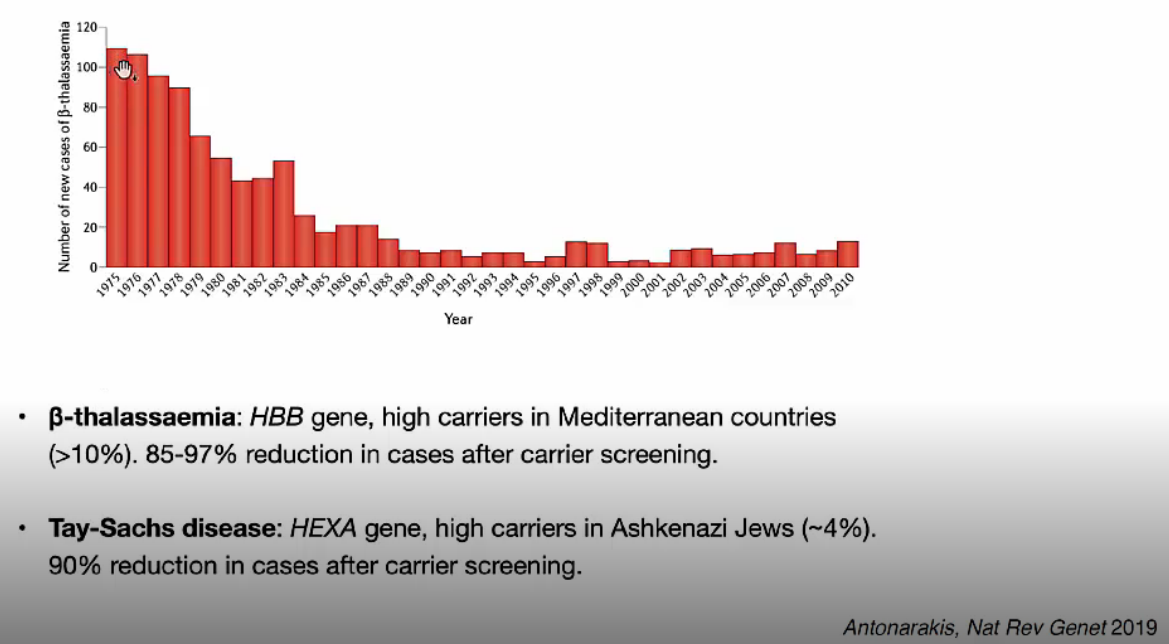
Recessive variants가 유발하는 대표적인 disease로 $\beta$-thalassaemia와 Ty-Sachs disease가 있습니다. 각각 HBB, HEXA gene의 variants로 유발되는 disease이며 specific population에서 높은 발병률을 보입니다. 어떤 recessive variants가 disease를 유발하는지 이해한 뒤로 보인자인 남녀가 결혼을 하거나 자녀를 출생하기 전 자녀의 disease 발병을 예방할 수 있습니다. 그래프에서 시간이 지남에 따라 $\beta$-thalassaemia의 새로운 환자 발병률이 점점 감소하는 것으로 볼 수 있습니다.
실제로 Myriad사에서는 Foresight Carrier Screen 서비스를 제공하고 있습니다. 175개 이상의 genetic diseases 대상으로 남녀의 carrier 보유 여부를 검사하고 결과를 제공합니다.
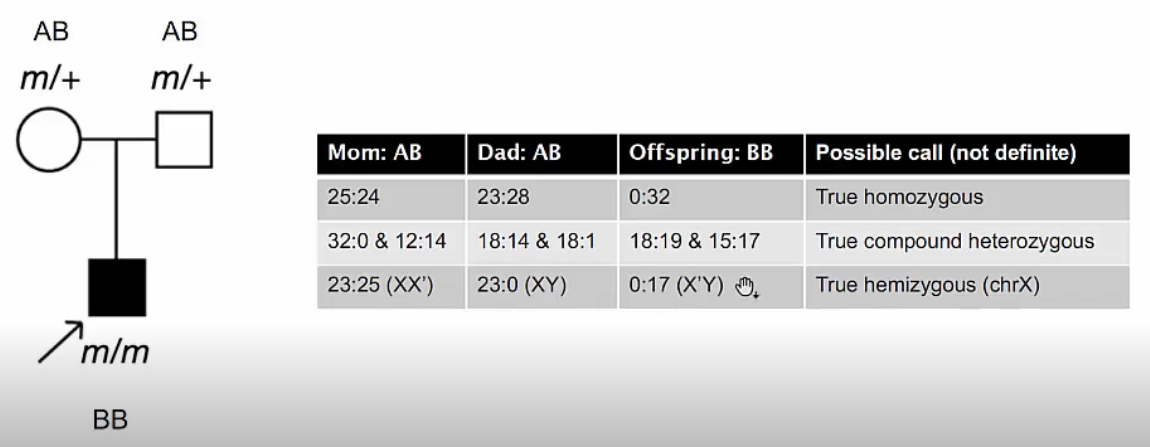
Call Compound Heterozygous Variants
Check reference coverage and non-reference coverage and calculate minor allele frequency(MAF)
$MAF = \frac{non-ref coverage}{(ref coverage + non-ref coverage)}$
MAF should be approximately 0.5
higher coverage the better
Check allele frequencies(AF) of genome databases like gnomAD, ExAC, 1000 genome, etc
다수의 정상인이 보유하고 있는 variants라면 disease를 유발할 가능성이 떨어집니다. 따라서 위와 같은 정상인 variants database에서 AF 0.01보다 작은 variants를 선별합니다.
One mutation should come from paternal. Another from maternal.
Call Rare Homozygous Variants
Check reference coverage and non-reference coverage and calculate minor allele frequency(MAF)
$MAF = \frac{non-ref coverage}{(ref coverage + non-ref coverage)}$
MAF should be very close to 1
higher coverage the better
Check allele frequencies(AF) of genome databases like gnomAD, ExAC, 1000 genome, etc
다수의 정상인이 보유하고 있는 variants라면 disease를 유발할 가능성이 떨어집니다. 하지만 정상인이 보유하고 있는 variants가 recessive 형태일 수 있고 결과적으로 환자가 가진 homozygous 형태에서는 AF가 그보다 높게 나타날 수 있습니다. 따라서 AF가 낮되 다른 recessive variants와 비교해서는 너무 낮지 않도록 고려합니다.
Call Hemizygous Variants
Check reference coverage and non-reference coverage and calculate minor allele frequency(MAF)
$MAF = \frac{non-ref coverage}{(ref coverage + non-ref coverage)}$
MAF should be approximately 1
higher coverage the better
Check allele frequencies(AF) of genome databases like gnomAD, ExAC, 1000 genome, etc
다수의 정상인이 보유하고 있는 variants라면 disease를 유발할 가능성이 떨어집니다. 따라서 위와 같은 정상인 variants database에서 AF 0.01보다 작은 variants를 선별합니다.
Should be very conserved
Check the number of different amino acid among species
Summary
- Recessive pattern을 따르는 variants는 Mendelian Disorder의 주요 병인으로 작용합니다.
- Recessive pattern을 따라는 variants 종류로는 homozygous, compound heterozygous, hemizygous variants가 있습니다.